Sectors in constant expansion such as Smart Cities, Industrial IoT (IIoT), and smart infrastructure projects are progressively increasing the demand for highly energy-efficient mobile radio technologies capable of transmitting data quickly and securely.
In this context, NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things) and LTE-M (Long Term Evolution for Machines) emerge as key connectivity technologies for the entire Internet of Things landscape. These technologies are designed to meet the needs of industries looking to integrate LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Networks) technology into their IoT devices to achieve long-range coverage with a reduced bitrate. This technology, thanks to its ability to significantly extend the battery life of devices and interconnect remote equipment, presents itself as a suitable solution for long-term “smart projects” oriented towards sustainability.
The differences: consumption and transmission speed
NB-IoT and LTE-M technologies are revolutionizing the communication landscape for the Internet of Things (IoT), offering specific solutions for different connectivity needs. While these solutions share similarities, it is also important to understand the differences between them.
The NB-IoT protocol, based on LTE standards, allows for progressive advancement towards network digitalization and the reliable and cost-effective connection of a vast number of devices. Thanks to its wide coverage and energy consumption optimization, NB-IoT is particularly suitable for applications with limited data transmission speed requirements and non-critical latency. Meanwhile, LTE-M, the latest generation of mobile IoT or LPWA (Low-Power-Wide-Area) technologies, utilizes the 4G cellular network and is characterized by wide coverage, stable performance even in mobility, and a higher data transmission capacity compared to Narrowband IoT. LTE-M, although potentially more costly and with higher energy demands than NB-IoT, stands out for its optimal performance in applications that require fast communications and substantial data transfers, such as industrial electric meters or real-time monitoring of electrical networks.
A global “challenge”
Among the numerous characteristics and functionalities required for wireless technologies, the availability of geographic connectivity on a global scale plays a crucial role. According to the latest data from the GSMA (Figure 1), there are a total of 162 LPWAN networks worldwide. Of these, 107 are dedicated to NB-IoT, while the remaining 55 are oriented towards LTE-M.
In regions with optimal LTE-M coverage, such as North America, IoT applications benefit from comprehensive support. However, in areas with limited coverage, NB-IoT may not fully meet the requirements of use cases due to its restrictions.
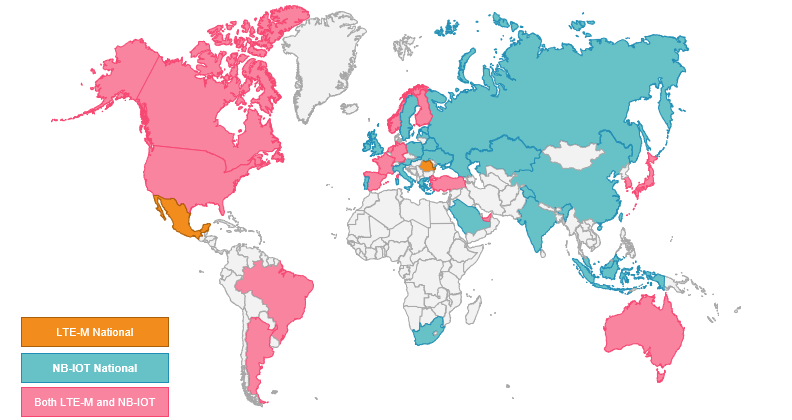
Fig 1 “GSMA: The latest “Mobile IoT Deployment Map”
In Europe, various IoT applications continue to rely on the 2G network because LTE-M coverage is still expanding. LTE-M can help stimulate sector growth as it offers a combination of reliable, long-range, and low-cost connectivity for IoT solutions. Its characteristics make this technology ideal for real-time asset monitoring over large areas without frequent battery replacements, and it can also provide reliable connectivity in challenging environments.
Onyax keeping pace with technological evolution
In this context, Onyax, through constant experimentation driven by the advanced technological demands of both the Italian and European markets, has integrated NB-IoT technologies into its dataloggers/IoT data acquisition devices from the outset. This has endowed its remote control solutions with rapid and efficient communication capabilities. Subsequently, Onyax has tested and implemented LTE-M technology in its solutions, opening up to the global market and responding to the growing needs of consumers and utilities, with a strong focus on sustainability and digitalization. In industrial sectors related to distribution networks such as Water and Oil & Gas, where specific characteristics are required, Onyax is continuously updating and demonstrating flexibility in adapting to the sector’s changes, which are becoming increasingly competitive and rapidly evolving.
Future projections
The future of the LTE-M and NB-IoT wireless module market offers opportunities and advantages stemming from the growing adoption of IoT devices, especially in sectors where ensuring reliable and scalable connectivity is essential. Projections foresee a significant increase in connections, rising from 436 million at the end of 2023 to 3.6 billion by 2032, significantly contributing to the evolution of a connected and intelligent IoT ecosystem. Thanks to their features that meet the stringent low-power and wide-area communication requirements of IoT applications, LTE-M and NB-IoT emerge as viable solutions for the specific needs of various operational contexts, thus paving the way for a future characterized by advanced connectivity and increasingly widespread smart applications.










